
How Long Does it Take to Recover From a Colonoscopy?
After a colonoscopy, patients are typically monitored in a recovery area until the effects of the sedative or anesthesia begin to wear off.
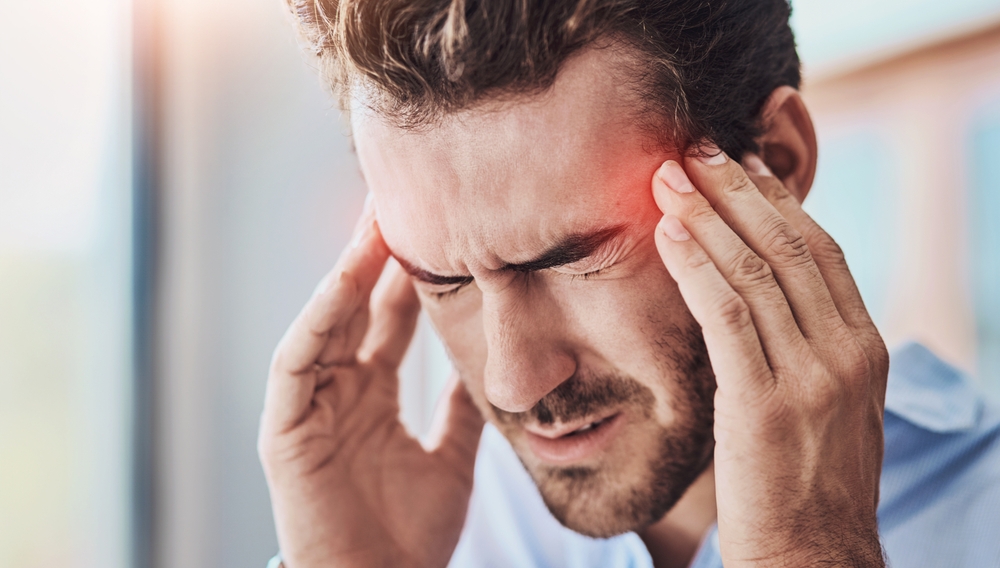

Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and migraines are two seemingly distinct conditions, yet research suggests there may be a strong connection between them. Both conditions are believed to involve complex interactions between the nervous and gastrointestinal systems. Shared triggers, such as stress, hormonal changes, and dietary factors, can exacerbate symptoms in both IBS and migraines.
Additionally, the gut-brain axis—a bidirectional communication system between the gut and the brain—plays a significant role in this connection, as disturbances in this pathway can potentially influence both digestive health and neurological activity. Understanding this link opens new possibilities for managing symptoms more effectively.
The gut-brain axis is a complex communication network that links the central nervous system (CNS) and the enteric nervous system (ENS). This bidirectional pathway ensures constant interaction between the brain and the gut, allowing them to influence each other’s functions. Signals are transmitted through various mechanisms, including the vagus nerve, the immune system, and the release of neurotransmitters and hormones. For example, serotonin, a key neurotransmitter, is not only vital for mood regulation but is also predominantly produced in the gut, highlighting the interdependence of these systems.
Disruptions in the gut microbiota—the community of microorganisms living in the digestive tract—can impact this axis, potentially contributing to conditions such as anxiety, depression, irritable bowel syndrome, and even migraines. By understanding this intricate relationship, researchers and clinicians can identify innovative strategies to address both digestive and neurological health concerns.
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) and migraines, though seemingly unrelated, share several common triggers that underline their potential connection.
Stress is a significant factor, as it can exacerbate symptoms in both conditions by influencing hormonal and neurological pathways.
Dietary choices also play a critical role, with certain foods, such as caffeine, chocolate, and processed items, frequently acting as triggers for both IBS flare-ups and migraine episodes.
Sleep disturbances, which affect the body’s natural rhythms, are another shared contributor, illustrating the interconnectedness of various bodily systems.
By identifying and managing these shared triggers, individuals can reduce the frequency and severity of symptoms associated with these conditions.
Inflammation is increasingly recognized as a key factor in both irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and migraines. While traditionally, IBS was considered a purely functional disorder without an inflammatory component, recent studies suggest that low-grade inflammation in the gut may contribute to its symptoms.
Similarly, migraines have been linked to neurogenic inflammation, a condition in which inflammation affects the nerves and blood vessels in the brain. Both conditions appear to be influenced by heightened immune responses and the release of pro-inflammatory substances, further connecting their underlying mechanisms. Understanding the role of inflammation in these conditions could pave the way for more targeted and effective treatment strategies.
Addressing IBS symptoms may play a role in reducing the frequency and severity of migraines.
Dietary adjustments, such as incorporating a low-FODMAP diet, can help minimize gut irritation and reduce inflammation. This, in turn, may positively impact migraine occurrence by stabilizing the gut-brain axis.
Probiotics and prebiotics that promote a healthy gut microbiome are also being explored as complementary approaches.
Managing stress through techniques like mindfulness, yoga, or cognitive-behavioral therapy may contribute to improved outcomes, as stress is a common trigger for both IBS and migraines. A holistic approach that targets both conditions could provide significant relief and enhance overall quality of life.
If you experience chronic symptoms that significantly impact your daily life, it may be time to consult a specialist. Persistent abdominal pain, bloating, frequent changes in bowel habits, or recurring migraines that do not improve with standard treatments warrant further evaluation.
Specialists such as gastroenterologists or neurologists can perform advanced diagnostic tests to identify underlying conditions and provide targeted treatment plans. Early intervention is crucial for managing symptoms effectively and preventing potential complications, thereby ensuring a better quality of life.
It is essential to know when to seek medical advice to address health concerns effectively. If you notice symptoms that persist, worsen over time, or interfere with your daily life, it may be time to consult your doctor. Signs such as unexplained weight loss, prolonged fatigue, or severe pain should not be ignored.
Please contact usat Allied Digestive Health if you see any sudden or alarming changes in your health, such as shortness of breath, chest pain, or unusual lumps, which require immediate attention. Being proactive about your health can lead to earlier diagnoses and better outcomes, allowing for quicker and more effective treatments.

After a colonoscopy, patients are typically monitored in a recovery area until the effects of the sedative or anesthesia begin to wear off.

Both conditions appear to be influenced by heightened immune responses and the release of pro-inflammatory substances, further connecting their underlying mechanisms.

A gut cleanse is a practice designed to enhance digestive health by removing toxins, waste, and harmful bacteria from the gastrointestinal tract.
The length of a flare-up often depends on multiple factors, including stress levels, dietary triggers, and the effectiveness of current management strategies.

Stomach ulcers are open sores that develop on the lining of the stomach or small intestine, but heartburn is caused when stomach acid flows back into the esophagus.

Poorly absorbed carbs may ferment in the gut, leading to symptoms such as bloating, gas, diarrhea, or constipation.

If left untreated, GERD can lead to complications including esophagitis (inflammation of the esophagus), strictures (narrowing of the esophagus), or even Barrett’s esophagus, a condition that increases the risk of esophageal cancer.

IBS-C often requires a tailored approach that incorporates dietary changes, stress management, and sometimes prescribed medications to regulate bowel movements and reduce discomfort.
Hepatitis C can affect women differently due to hormonal variations, immune system responses, and unique physiological factors

This connection means that stress, anxiety, and other psychological factors can directly impact gut function, leading to symptoms like abdominal pain, bloating, and irregular bowel movements.

Chronic inflammation associated with IBD can lead to complications such as joint pain, skin conditions, eye issues, and more.

How different types of fiber affect IBS is crucial to creating a diet that supports digestive health without triggering flare-ups.
For Your Visit
Brick Office
P: 732-458-8300
Brick Medical Arts Building
1640 Route 88, Suite 202
Brick, New Jersey 08724
Mon – Fri: 8:30AM – 5:00PM
Sat & Sun: Closed
Neptune Office
P: 732-776-9300
Jersey Shore Medical Arts Building
1944 Corlies Ave. Suite 205
Neptune, New Jersey 07753
Mon – Fri: 8:30AM – 5:00PM
Sat & Sun: Closed
Jackson Office
P: 732-928-2300
706 Bennetts Mills Road
Jackson, New Jersey 08527
Mon – Fri: 8:30AM – 5:00PM
Sat & Sun: Closed
© All Rights Reserved