
Signs of Stomach Ulcers
Stomach ulcers are open sores that develop on the lining of the stomach or small intestine, but heartburn is caused when stomach acid flows back into the esophagus.
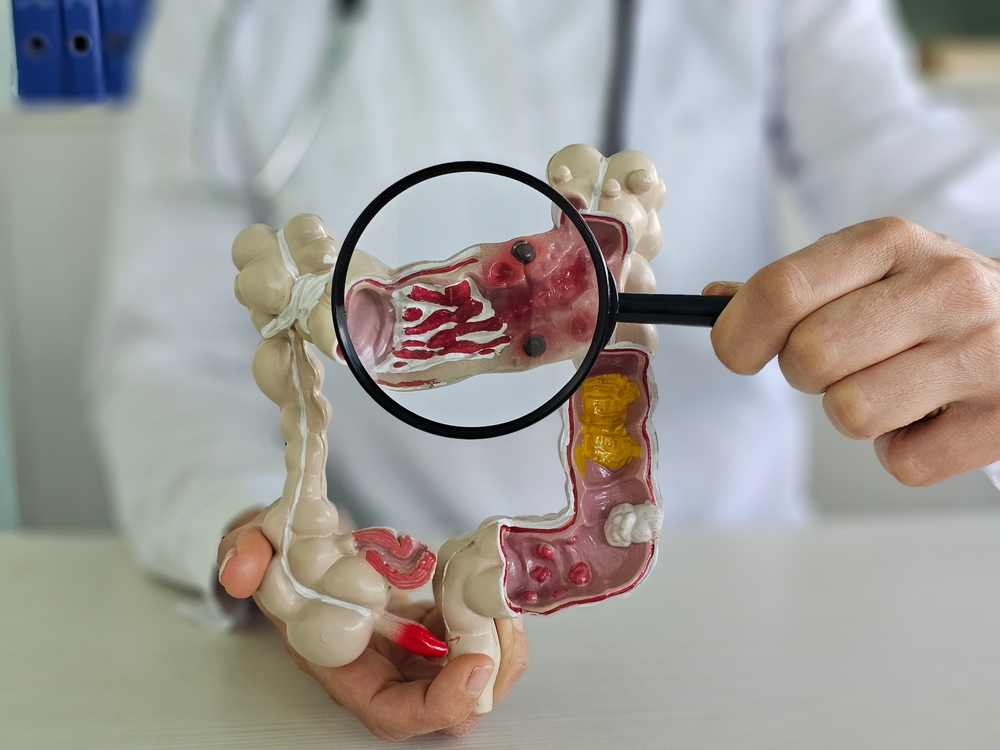
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) and colon cancer share several overlapping symptoms, which can make it challenging to differentiate between the two without medical evaluation. Both conditions may present with abdominal pain, changes in bowel habits, weight loss, and rectal bleeding. However, the underlying causes and progression of these diseases are distinct. IBD, which includes Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, is a chronic inflammatory condition of the gastrointestinal tract, often driven by an overactive immune response.
Colon cancer results from abnormal cell growth in the colon or rectum that leads to the formation of malignant tumors. Recognizing early warning signs and undergoing appropriate screenings is crucial to ensure accurate diagnosis and effective treatment. Consulting a healthcare provider is essential to differentiate symptoms and determine the best action.
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) is a group of chronic conditions characterized by inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract. The two main types of IBD are Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis.
Crohn’s disease can affect any part of the digestive tract, from the mouth to the anus, and often involves inflammation that extends through multiple layers of the gut wall. Ulcerative colitis, on the other hand, primarily impacts the colon and rectum, causing inflammation and ulcers in the innermost lining.
While the exact cause of IBD remains unclear, factors such as genetics, immune system dysfunction, and environmental triggers are believed to contribute. Symptoms of IBD commonly include abdominal pain, diarrhea, fatigue, and unintended weight loss, though the severity and frequency of these symptoms can vary significantly between individuals.
Colon cancer, also known as colorectal cancer, can present with a variety of symptoms, some of which may overlap with other digestive conditions.
Common signs include persistent changes in bowel habits, such as diarrhea, constipation, or stool consistency. Individuals may also experience rectal bleeding or notice blood in their stool, which can appear bright red or dark.
Other symptoms include unexplained weight loss, fatigue, and ongoing abdominal discomfort, such as cramping, gas, or pain. Symptoms may often go unnoticed in the early stages, so regular screenings are crucial for early detection and improved treatment outcomes.
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) and colon cancer share several symptoms, making it challenging to differentiate between the two conditions without thorough medical evaluation. Both conditions can present with rectal bleeding, changes in bowel habits, abdominal pain, and unintentional weight loss. Fatigue and a general sense of discomfort can occur in both cases.
These overlapping symptoms highlight the importance of consulting a healthcare professional for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Screening tests and diagnostic procedures such as colonoscopy, imaging, and biopsies are essential in distinguishing between IBD and colon cancer.
Understanding the risk factors for both IBD and colon cancer is essential for prevention and early intervention. For IBD, genetics play a significant role, as individuals with a family history of the condition are at higher risk. Environmental factors, such as diet, smoking, and stress, can also contribute to the development or exacerbation of IBD.
Colon cancer risk increases with age, typically affecting individuals over 50, though younger people with certain risk factors may also be vulnerable. Lifestyle factors like a diet high in processed foods and red meat, lack of physical activity, obesity, smoking, and excessive alcohol consumption significantly contribute to colon cancer risk.
A history of IBD itself can heighten the risk of developing colon cancer over time, emphasizing the importance of regular monitoring and proactive healthcare measures for those with chronic inflammatory conditions.
Diagnosing IBD and colon cancer involves a combination of patient history, physical examinations, laboratory tests, and advanced imaging techniques. For IBD, physicians typically begin by evaluating symptoms such as abdominal pain, diarrhea, and weight loss. Blood and stool tests are commonly used to check for signs of inflammation or infection.
Endoscopic procedures, like colonoscopy and sigmoidoscopy, are essential for visualizing the intestinal lining and obtaining biopsies to confirm the presence of inflammation or other abnormalities.
For colon cancer, screening plays a vital role in early detection, especially for individuals over the age of 50 or those with identifiable risk factors. A colonoscopy is the gold standard for identifying polyps or cancerous growths within the colon. Additional diagnostic tools such as CT colonography, stool-based tests (e.g., FIT or Cologuard), and imaging scans like CT or MRI may be utilized to detect tumors or assess disease progression. Early and accurate diagnosis significantly improves outcomes for patients with either condition, making routine check-ups and screenings crucial.
Living with concerns related to digestive health can often lead to feelings of anxiety or stress, especially when symptoms persist or require ongoing medical attention. One practical approach to managing this anxiety is to stay informed about your condition and work closely with healthcare professionals to address any questions or uncertainties. Developing a routine that includes proper nutrition, regular physical activity, and adequate sleep can also help reduce stress and support overall digestive health.
Relaxation techniques such as mindfulness meditation, yoga, or deep-breathing exercises can be invaluable in managing anxiety. Seeking support from friends, family, or professional counselors may provide emotional relief and encouragement, creating a balanced approach to mental and physical health.
It’s essential to know when to seek medical advice regarding digestive health. You should consider consulting your doctor if you experience persistent or worsening symptoms such as severe abdominal pain, unexplained weight loss, chronic diarrhea, or blood in your stool. Additionally, recurring symptoms like heartburn, bloating, or changes in bowel habits that disrupt your daily life may require professional evaluation. Early intervention can help identify potential underlying conditions and prevent complications. Don’t hesitate to contact your healthcare provider if your symptoms cause significant worry or interfere with your quality of life, as timely medical attention can lead to better outcomes and peace of mind. When in doubt, feel free to talk to the professionals at Allied Digestive Health.

Stomach ulcers are open sores that develop on the lining of the stomach or small intestine, but heartburn is caused when stomach acid flows back into the esophagus.

Poorly absorbed carbs may ferment in the gut, leading to symptoms such as bloating, gas, diarrhea, or constipation.

If left untreated, GERD can lead to complications including esophagitis (inflammation of the esophagus), strictures (narrowing of the esophagus), or even Barrett’s esophagus, a condition that increases the risk of esophageal cancer.

IBS-C often requires a tailored approach that incorporates dietary changes, stress management, and sometimes prescribed medications to regulate bowel movements and reduce discomfort.
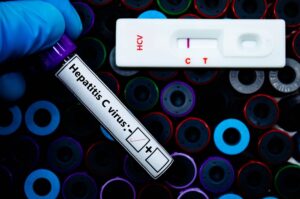
Hepatitis C can affect women differently due to hormonal variations, immune system responses, and unique physiological factors

This connection means that stress, anxiety, and other psychological factors can directly impact gut function, leading to symptoms like abdominal pain, bloating, and irregular bowel movements.

Chronic inflammation associated with IBD can lead to complications such as joint pain, skin conditions, eye issues, and more.

How different types of fiber affect IBS is crucial to creating a diet that supports digestive health without triggering flare-ups.

Lactose Intolerance occurs due to a deficiency of lactase, the enzyme responsible for digesting lactose in the small intestine.
This condition can result from various factors, including poor diet, stress, infections, or underlying health conditions like IBD.

One of the most essential steps in managing IBS is identifying specific triggers and paying attention to your body’s unique responses.

Although the symptoms of IBS can vary widely from person to person, several common signs are associated with the condition.
For Your Visit
Brick Office
P: 732-458-8300
Brick Medical Arts Building
1640 Route 88, Suite 202
Brick, New Jersey 08724
Mon – Fri: 8:30AM – 5:00PM
Sat & Sun: Closed
Neptune Office
P: 732-776-9300
Jersey Shore Medical Arts Building
1944 Corlies Ave. Suite 205
Neptune, New Jersey 07753
Mon – Fri: 8:30AM – 5:00PM
Sat & Sun: Closed
Jackson Office
P: 732-928-2300
706 Bennetts Mills Road
Jackson, New Jersey 08527
Mon – Fri: 8:30AM – 5:00PM
Sat & Sun: Closed
© All Rights Reserved